The Chassis Parts Industry in China
The industry is growing rapidly, but manufacturers face size and R&D problems
2013/04/08 | By CENSThe chassis parts segment has been gaining an increasingly important role in China's overall automotive industry, especially after the country's accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO). Lucrative business opportunities beckon, but the relatively immature segment is also expected to face many uncertainties in its future development.
Statistics compiled by the National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC) show that the chassis-parts industry has been enjoying a growth of 15% annually in recent years. According to the latest data released by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), more than 19 million new cars were sold in China in 2012, indicating that there is obviously a huge demand for chassis parts.
However, industry sources say, China's chassis-parts industry still faces some big challenges, including soaring steel prices, rising labor costs, falling market prices (due to fierce competition), difficulty in exploring export markets, and the control of key technologies by big international companies.
The largest number of China's automotive chassis-parts manufacturers is clustered in Zhejiang Province, which accounts for about 25% of the country's total chassis-parts production. Other cities and provinces with clusters for making chassis parts include Jiangsu, Beijing, Jilin, Hubei, and Shandong. Their products have a local-content ratio of only about 30%; since many of the parts require relatively high technology to make, a major portion of them has to be imported.
Drive by Wire
Chassis parts are related to many other vehicle systems, including brakes, steering, and suspension. Several advanced technologies are currently leading development trends, including overall chassis control, vehicle open-architecture engineering, and "X-by-wire."
In "X-by-wire", industry sources say, the top priority is to further improve steering capability. Many international automakers and tier-one parts suppliers have been aggressively developing such systems, which control brakes, steering, acceleration, and other systems via electrical wires (by sending signals from computers) rather than by the complicated mechanical systems generally used today.
One out of every two new passenger cars and light commercial vehicles produced in Europe and the United States today is equipped with an electronic stability program (ESP) safety system, and governments are expected to demand such a system in all new vehicles in the future.
All vehicles weighing less than 4.5 tons sold in the United States since Sept. 2012 have had to be equipped with ESP, and all passenger cars and light, medium, and heavy vehicles sold in Europe will be required to have such safety protection beginning in Nov. 2014. Only about 11% of all cars produced in China today are equipped with ESP, but the ratio is expected to rise rapidly over next few years.

A Problem of Size
The chassis-parts industry in China suffers from a number of disadvantages. The first is the small scale of its manufacturers. More than 70% of them have annual revenues of less than 100 million renminbi (RMB, or Chinese yuan); for private producers the ratio is 89%, and for Chinese-foreign joint ventures it is 61%. Only about 7% of all chassis-parts makers in China have annual revenues or 500 million to 1 billion RMB.
In addition, the industry is at a relatively low level of the international division-of-labor scheme, and most higher-end products have to be imported.
Finally, the R&D capability of China's chassis-parts industry is weak, and more than 70% of the producers do not own patents.
Future Challenges
China became the world's largest automobile market in 2009, and annual new-car sales there have topped 18 million units for three years in a row. The CAAM predicts that new-car sales will top 20.65 million units this year, up 7% from 2012.
The rapidly developing automobile market in China will bring strong opportunities for the chassis-parts industry, but manufacturers in the line will have to further strengthen their R&D strength, upgrade their innovation, develop their own brands, expand their markets, and enhance their competitiveness.
Zhejiang DLZ
One of the foremost chassis-parts makers in China is the Zhejiang DLZ Machinery Manufacturing Co. (DLZ). Founded in 1991, DLZ is a globally known supplier of suspension parts mainly for the aftermarket, and its own “DLZ” brand has been officially registered in more than 100 countries.
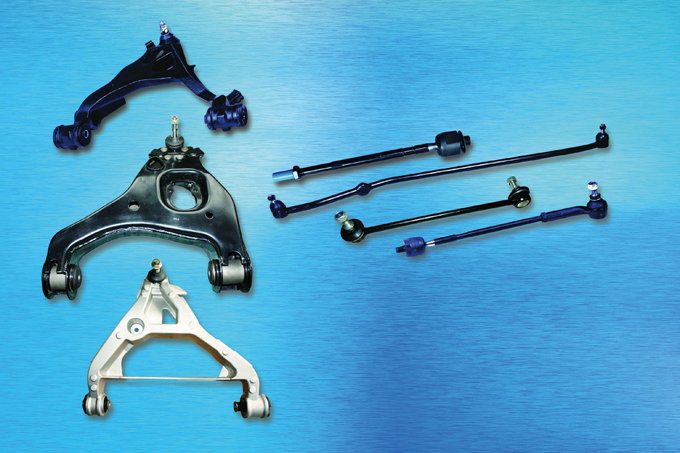
The company's product portfolio covers a wide spectrum of suspension parts, including ball joints, tie rod ends, rack ends, stabilizer links, idler arms, pitman arms, control arms, drag links, and bushings. The products come in over 7,000 different specifications and sizes for use in Chinese, Japanese, American, European, and Korean cars.
The company has successfully tapped export markets in some 20 countries of America, Europe, Asia, and Africa with its own-brand products, and has built partnerships with large international suppliers for the joint development of suspension system technologies.
One of DLZ's competitive advantages is its large production capacity. With more than 500 workers, including some 30 experienced R&D engineers and 40 QC staffers, the company is able to turn out 500,000 sets of suspension parts, and adds 50 new items to its list of available products, every month.
Honssion
Another top Chinese supplier is Honssion Auto Chassis System (Zhejiang) Co., Ltd., which supplies a wide array of products including ball Joints, tie rod ends, rack ends, tie rod assemblies, control arms, and stabilizer links.
Ever since its inception in 1993, Honssion has specialized in making chassis and steering system parts, all developed using advanced computer technologies to assure reliable, unbeatable quality.
CAD (computer aided design), CAM (computer aided manufacturing), and UG (Unigraphics) are among the latest computer technologies that the company uses to develop and produce a variety of chassis system and steering system parts. The products are available in over 2,000 different specifications and sizes, suiting them to nearly all European, Japanese, and American cars. Honssion is currently capable of turning out 25,000 parts per day.