Mazda Unveils World's 1st Capacitor-Based Regenerative Braking System for Passenger Vehicles
2012/03/01 | By Quincy LiangWith fuel efficiency and carbon reduction becoming top proprieties in the global automotive industry, automakers everywhere are working aggressively to introduce cars that incorporate the latest technologies to achieve these goals.
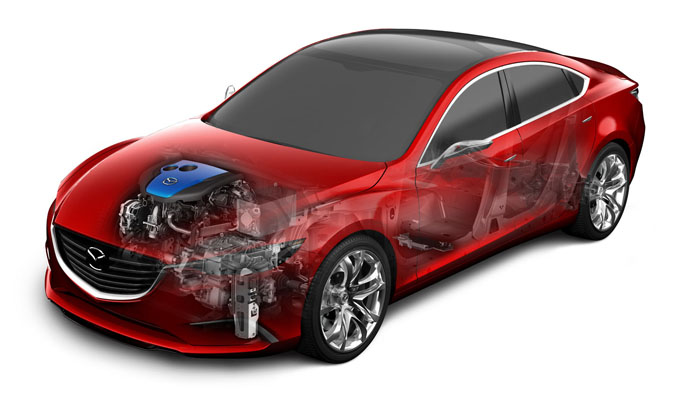

One recent example of this effort is Mazda Motor's 'i-ELOOP', which the firm claims is the world's first passenger vehicle regenerative braking system that uses a capacitor. This new system will appear in Mazda vehicles beginning in 2012, improving fuel economy by approximately 10%.

Mazda says that its regenerative braking system is unique because it uses a capacitor, which is an electrical component that temporarily stores large volumes of electricity. Compared to batteries, capacitors can be charged and discharged rapidly and are resistant to deterioration through prolonged use. The 'i-ELOOP' efficiently converts a vehicle's kinetic energy into electricity as it decelerates, and uses the electricity to power the vehicle's climate control, audio system, and other electrical components. Regenerative braking systems are growing in popularity as a fuel-saving technology.
They use an electric motor or alternator to generate electricity as the vehicle decelerates, thereby recovering a portion of the vehicle's kinetic energy. Regenerative braking systems in hybrid vehicles generally use a large generator and dedicated battery.
Mazda says it examined automobile acceleration and deceleration mechanisms, and developed a highly efficient regenerative braking system that rapidly recovers a large amount of electricity every time the vehicle decelerates. Unlike hybrids, Mazda's system avoids the need for a dedicated generator and battery.

The 'i-ELOOP' features a new 12-25V variable voltage alternator, a low-resistance electric double-layer capacitor, and a DC/DC converter. The system starts to recover kinetic energy the moment the driver lifts off the accelerator pedal and the vehicle begins to decelerate. The variable voltage alternator generates electricity at up to 25V for maximum efficiency before sending it to the Electric Double Layer Capacitor (EDLC) for storage. The capacitor, which has been specially developed for use in a vehicle, can be fully charged in seconds. The DC/DC converter steps down the electricity from 25V to 12V before it is distributed directly to the vehicle's electrical components. The system also charges the vehicle battery as necessary. Since the 'i-ELOOP' operates whenever the vehicle decelerates, it reduces the need for the engine to burn extra fuel to generate electricity. As a result, in "stop-and-go" driving conditions, fuel economy improves by approximately 10%.
Mazda explains that the name 'i-ELOOP' is an adaptation of "Intelligent Energy Loop" and represents the automaker's intention to efficiently cycle energy in an intelligent way.
'i-ELOOP' also works in conjunction with Mazda's unique 'i-stop' technology to extend the period that the engine can be shut off.
Mazda says that it is working to maximize the efficiency of internal combustion engine vehicles with its groundbreaking “Skyactive Technology.” By combining this with i-stop, i-ELOOP, and other electric devices that enhance fuel economy by eliminating unnecessary fuel consumption, Mazda is striving to deliver vehicles with excellent environmental performance.