EV Taiwan 2012 Shows Electrifying R&D Work by TARC
2012/11/02 | By Quincy LiangWithout world-class automakers in Taiwan, where operators have always been OEMs for global brands except for the Luxgen line that was launched in the last couple of years by the local Yulon Group to claim to be the first homegrown vehicle built on an SUV platform, literally all the automotive R&D on the island is conducted mainly by officially-backed research institutes, with some undertaken by leading auto-parts manufacturers.
This year's Taiwan Int'l Electric Vehicle Show (EV Taiwan 2012) saw, in addition to displays by domestic and international manufacturers, the fruits of R&D of the Taiwan Automotive Research Consortium (TARC).
EV Taiwan 2012 was held alongside the 2012 Taiwan International Motorcycle Industry Show (Motorcycle Taiwan 2012) April 12-15, overlapping the 2012 Taipei International Auto Parts & Accessories Show (Taipei AMPA) and Taipei International Automobile Electronics Show (AutoTronics Taipei), held April 11-14 at the Taipei World Trade Center Nangang Exhibition Hall.
TARC
To tap synergy by pooling the resources of industrial, governmental, academic and research sectors in Taiwan to jointly develop the automotive industry, the Department of Industrial Technology (DoIT) of the Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA) urged the four key research institutes to establish the TARC in mid-2005, whose six members consist of the Automotive Research and Testing Center (ARTC), the Mechanical and System Research Laboratories (MSL) of Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI), the Material and Chemical Research Laboratories (MCL) of ITRI, the Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology (CSIST), and Hua-chuang Automobile Information Technical Center Co. Ltd. (HAITEC).
The key goals of the TARC are to establish an integrated platform for automotive technological R&D; assist the domestic industry to set up a concurrent engineering design platform through international cooperation and technology transfer; and work with local universities to train personnel and set up a platform for innovative research.
In recent years and meeting the rising eco trend globally, the TARC aims to integrate the above-mentioned platforms and their technologies to develop electric vehicles and upgrade their intelligence.
The TARC Pavilion at the EV Taiwan 2012 has several major themes, including EV, key module, smart component and service platform that revolve around Green Energy and Intelligence, many items of which being concepts, prototypes and ready for commercialization, proving to be an excellent publicity event too for the TARC and the future direction of its work.

Surprising Power
The electric motorcycle has high torque and acceleration comparable to those of a 750cc internal combustion engine (ICE) counterpart, with electric propulsion protected by a 96V high-voltage system with diagnostic, control and automatic power-off to greatly enhance safety. Weighing 260 kg with maximum speed of 120 kph and cruise range of 80 km that uses 96V, the e-motorbike is powered by a 25KW or 33.5 horsepower motor.
The digital dashboard features personalized graphic interface and real-time display of operational conditions, with the driving-safety protection providing real-time warning, as well as power-saving function in the low-power standby, while the 1280x480 LCD interface displays real-time cam-fed video.
The ITRI-developed electric-scooter battery swapping system features a user-friendly revolving battery-pack exchange.

The universal EV chassis jointly developed by the TARC and MIRDC offers unprecedented flexibility for assembled-EV developers. Including the front, center and rear structures, the chassis' front and central parts are designed to be open to enable compatibility with various propulsion systems and battery modules, hence allowing maximum freedom to EV developers to develop various assembled EVs, such as low-speed vehicle (four-wheeled vehicles with maximum speed of around 25 mph), sedans and sport utility vehicles (SUV) with different horsepower and cruise ranges. Such chassis, most importantly, enables makers to more easily fill small-batch, large-variety orders.
The wheelbase of the chassis can range 2,500mm to 2,800mm, the power module 50-150KW, and the battery module 18-36 kWh, with the lightweight structure being high-strength steel (about 70%) and aluminum alloy (10%).
Intelligent Modules
An intelligent bi-directional 6kW DC/DC converter for rechargeable battery system was shown, which charges and discharges multiple DC power sources and devices as well as works with power management controllers for renewable energy storage. The main features include the bi-directional dynamic power regulation, the buck and boost control, switch control for constant current and voltage modes, and protection mechanisms for both charger and discharger modes.
The TARC and ITRI jointly developed the 40Ah high-capacity, energy density, and safe lithium-ion battery cell and pack; while the ITRI also showcased a 50kW EV motor controller with extended range of maximum constant power, high power density and high efficiency, wide-range EV motor controller, precision low-speed control, high-torque mode, and safety protection and diagnostic technology for electrical propulsion.
Smart Components
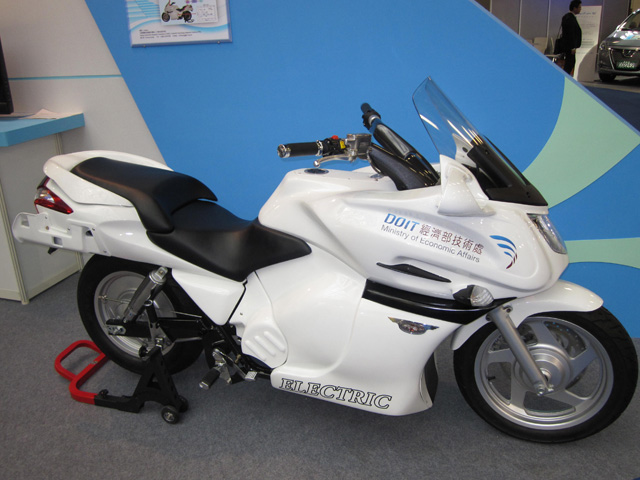
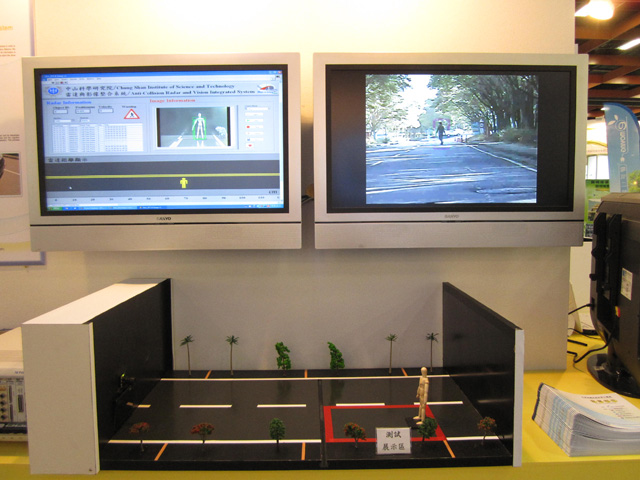
The vehicle rolling warning system (VRWS) uses advanced image-recognition and vehicle dynamic measurement technologies to determine curvature of road, reducing effectively risk of vehicle rollover on curved roads by estimating the rollover index and maximum rollover threshold in real time via the vehicle slip angle, vehicle speed, acceleration, steering angle and roll angle etc. Its interfaces include CAN BUS (steering angle sensor and gyroscope) and CVBS (camera).
The anti-collision radar and vision integrated system developed by the CSIST adopts the pedestrian detection technology by analyzing frontal camera images as well as dynamic information as relative distance, speed, angle. Warning signals alert the driver accordingly to reduce risk of hitting pedestrians.
The CSIST also showed a glare detection system to prevent traffic accidents due to driver's visions being impaired by glare, claiming glares delay driver's reaction time and impede vision temporarily to potentially cause accidents. The institute uses multi-segment image processing and the optical drop filter system to effectively offset frontal glare.

Better Safety
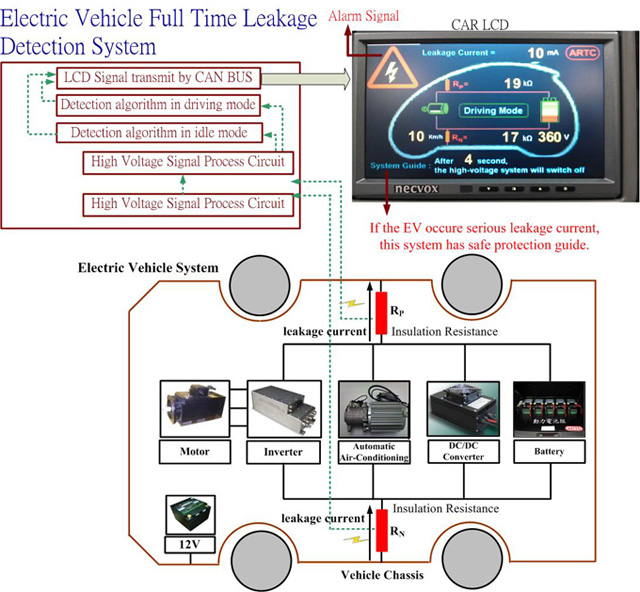
The full-time EV leakage detection system is designed to help EVs achieve better safety. EVs use high-voltage DC as power that can potentially leak to shock and injure drivers. Therefore the ARTC says a leakage detection system is very important.
The system measures insulation resistance and current leakage between the high-voltage power system and chassis while idling or driving. If insulation resistance exceeds the safe value, the system alerts the driver and, in the absence of response, shuts down the power system. Unlike other systems that operate only in idle, the ARTC system, due to various circuits and algorithms, also works in driving mode to ensure total safety.
The TARC also demonstrated two EV service platforms including the Taiwan EV Supply Chain and EV Monitoring & Service Platform. The former is an online platform established by the Department of Industrial Technology (DoIT) and TARC to promote Taiwan's EV supply chain to enhance EV industrial cooperation and development. The latter offers services to fleets and private EV owners.